

Some laboratories use safranin as a counterstain however, basic fuchsin stains gram-negative organisms more intensely than safranin. The final step in gram staining is to use basic fuchsin stain to give decolorized gram-negative bacteria pink color for easier identification. The length of decolorization is a critical step in gram staining as prolonged exposure to a decolorizing agent can remove all the stains from both types of bacteria. In contrast, solvent dehydrates the gram-positive cell walls with the closure of pores preventing diffusion of violet-iodine complex, and thus, bacteria remain stained. It should be noted, however, that Gram staining can be variable.

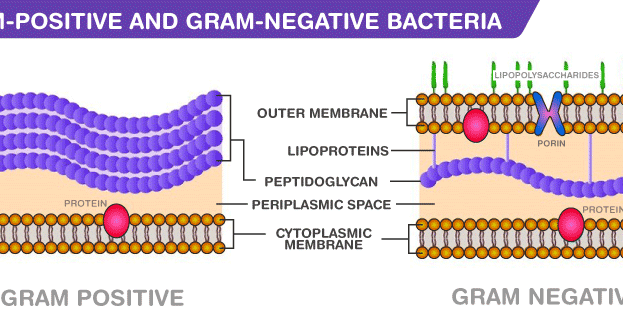
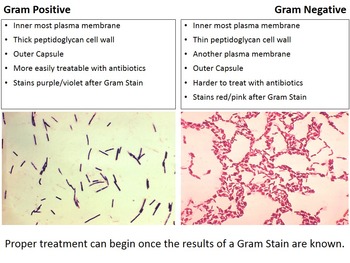
With the dissolution of the lipid layer, gram negatives lose the primary stain. Gram-negative bacteria will stain pink/red and Gram-positive bacteria will stain blue/purple. Initially, all bacteria take up crystal violet dye however, with the use of solvent, the lipid layer from gram-negative organisms is dissolved. Gram-positive microorganisms have higher peptidoglycan content, whereas gram-negative organisms have higher lipid content. The basic principle of gram staining involves the ability of the bacterial cell wall to retain the crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. Subsequently, a decolorizer, often solvent of ethanol and acetone, is used to remove the dye. Gram-negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer. The next step, also known as fixing the dye, involves using iodine to form crystal violet- iodine complex to prevent easy removal of dye. Differential stains are able to differentiate between gram-positive and gram-negative cells. The first step in gram staining is the use of crystal violet dye for the slide's initial staining. The organisms that do not take up primary stain appear red under a microscope and are Gram-negative organisms. The term for organisms that retain the primary color and appear purple-brown under a microscope is Gram-positive organisms. Often the first test performed, gram staining involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color. The differential nature of the Gram stain is based on the ability of some bacterial cells to retain a primary stain (crystal violet) by resisting a decolorization. It gets its name from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia. Today we use Gram’s staining techniques to aid in the identification of bacteria, beginning with a preliminary classification into one of two groups: Gram positive or Gram negative. “ Acinetobacter in Healthcare Settings.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.The Gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. “ Haemophilus influenzae serotype f endocarditis and septic arthritis.” IDCases, vol. “ Molecular pathogenesis of infections caused by Moraxella catarrhalis in children.” Swiss Medical Weekly, 29 Oct. These categories are based on their cell wall composition and reaction to the Gram stain test. “ Gonorrhea - CDC Fact Sheet (Detailed Version).” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.īernhard, Sara, et al. By Regina Bailey Updated on FebruMost bacteria are classified into two broad categories: Gram positive and Gram negative. “ Pathogenesis of Meningococcemia.” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, vol. “ Endotoxin Elimination in Patients with Septic Shock: An Observation Study.” Archivum Immunologiae Et Therapiae Experimentalis, vol. “ Group A Streptococcal (GAS) Disease.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.Īdamik, Barbara, et al. “ Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA).” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “ Bacterial Biofilm Formation on Implantable Devices and Approaches to Its Treatment and Prevention.” Heliyon, vol.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
